When it comes to hosting a website, one of the most crucial decisions you’ll need to make is choosing the right web server software. A web server is a software that serves users with web content and allow them to view the website on the internet.
And you probably would have noticed how various web hosting companies advertise what web server technology they provide. That itself shows how important a web server is to a website.
Among the many web servers available, LiteSpeed, Apache, and Nginx stand out as some of the most popular options. These are the popular options for all the right reasons, but they do have some subtle differences and these differences will make you choose one over the other.
Your choice can significantly impact your website’s performance, security, and scalability.
In this blog post, we’ll compare these three web servers to help you determine which one is the right choice for your specific needs.
What is Web Servers?
A web server is a software that stores and runs all the files that make up a website. It handles all the client requests and delivers the web content the client asks for.
It’s essentially the bridge between your website’s files and the people who want to access them.
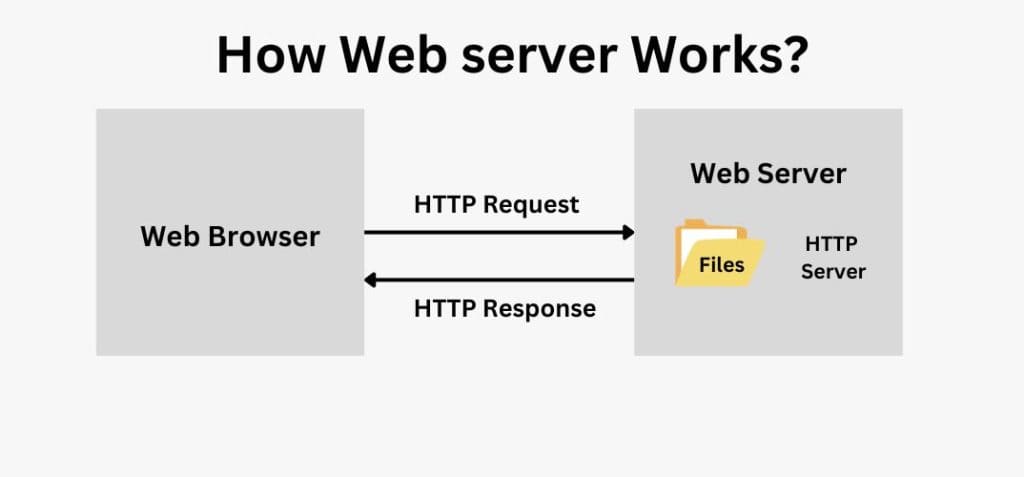
For example, when someone wants to find a file, they will search for that using a web browser. The file they searched for will be hosted on a web server and the browser will request that file via HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). Then this request will reach the web server, it will accept the request, find the requested file, and send it back to the client. And when a server can’t find the requested document, that’s when it will return a 404 error.
A 404 error is when a website’s server can’t find the requested page
Nginx

Nginx (pronounced “engine-x”) is a relatively newer player among the web servers, first released in 2004. It was created with a goal, that is to outperform Apache, which it did and became the most popular web server technology.
In the beginning, it used to work along with Apache as a load balancer or as a reverse proxy for busy websites. In essence, it merely helped web servers balance the load of requests.
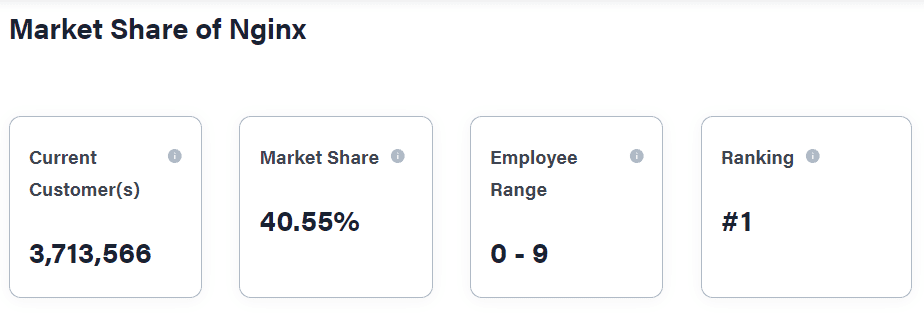
But now, it’s software has evolved, and Nginx works alone as an independent web server. Over the years, it has achieved a lot more than it intended to, with a market share of whooping 40.55% and growing while ranking No.1 among all the web servers.
Pros of Nginx:
- High Performance: Nginx excels at serving static content quickly, making it ideal for websites with heavy traffic loads.
- Low Memory Usage: Nginx is known for its minimal memory usage, making it efficient even on servers with limited resources.
- Reverse Proxy: Nginx can also function as a reverse proxy, handling requests to other web servers or applications.
Cons of Nginx:
- Limited Dynamic Content Handling: While Nginx can serve static content efficiently, it may require additional configuration or modules to handle dynamic content effectively.
- Steeper Learning Curve: Nginx’s configuration syntax can be intimidating for beginners.
Apache

Apache, short for Apache HTTP Server, has been around since 1995 and has a long-standing reputation as a reliable and feature-rich web server.
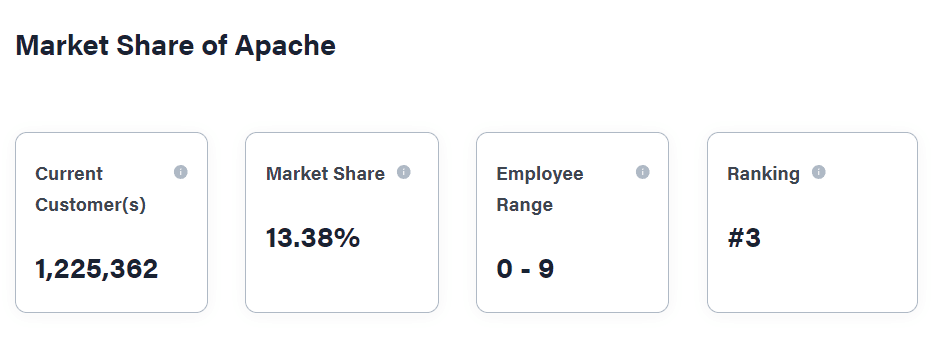
It’s open-source and free to use, making it a popular choice among web hosting providers. It is one of the most widely used web servers.
One reason for Apache being one of the most used web server is that it is preinstalled on all major Linux servers, which makes it easy to get it up and run it as the web server technology. It is also comparatively easier to set it up and a little knowledge of hosting is enough to get the job done.
Pros of Apache:
- Mature Technology: Apache has been tried and tested for decades, making it a dependable choice for web hosting.
- Extensive Documentation: There is an abundance of documentation and community support available for Apache, making it beginner-friendly.
- Module Support: Apache’s modular architecture allows for the integration of various extensions to add functionality.
Cons of Apache:
- Resource Intensive: Apache can be resource-intensive, especially when handling a high volume of concurrent connections.
- Configuration Complexity: Configuring Apache can be complex, and inexperienced users may find it challenging to set up. But setting up is much easier compared to Nginx
LiteSpeed

LiteSpeed was first introduced in 2003. It’s gained attention for its innovative approaches to web server technology, aiming to deliver high performance, scalability, and security. You can fine-tune your website’s performance with LiteSpeed, it offers options for caching and compressing.
It can run double the number of websites and can deliver content 50 times faster compared to Apache. Thus, LiteSpeed is perfect for websites that get a visitors or a website with a lot of digital content.
It is also one of the most scalable option available among web servers, you can ensure you website stays active during peak hours or when encountered with a sudden customer spike.
Pros of LiteSpeed:
- High Performance: Like Nginx, LiteSpeed is known for its speed and can handle high traffic loads efficiently.
- LiteSpeed Cache: Offers built-in caching solutions that can significantly enhance website performance.
- Security Features: LiteSpeed includes security features like mod_security rules and DDoS protection.
Cons of LiteSpeed:
- Licensing Costs: While there is a free open-source version of LiteSpeed, the most feature-rich version comes with a licensing fee.
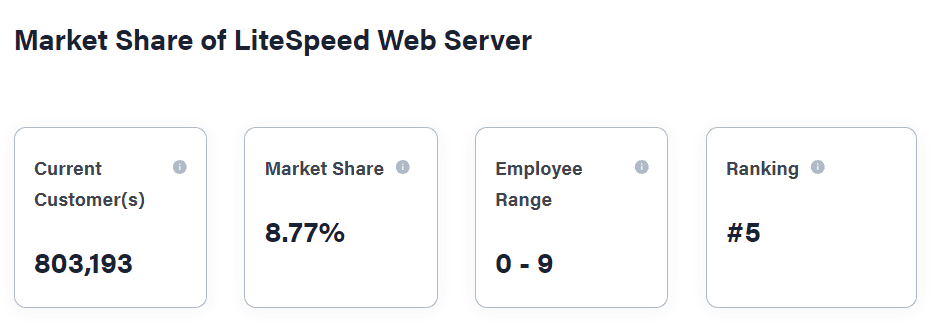
- Smaller User Base: LiteSpeed has a smaller user base compared to Apache and Nginx, which may mean fewer resources and community support.
Choosing the Right Web Server for You
Now that we’ve explored the strengths and weaknesses of LiteSpeed, Apache, and Nginx, how do you decide which one is right web server choice for your needs?
Here are some factors to consider:
1. Performance Requirements:
- If you expect high traffic and need excellent performance, Nginx or LiteSpeed may be better choices.
- For smaller websites with lower traffic, Apache can still perform well.
2. Resource Availability:
- If you have limited server resources (e.g., RAM), Nginx or LiteSpeed’s efficiency may be advantageous.
- Apache can be resource-intensive, so it may require more powerful hardware.
3. Ease of Use:
- Apache’s extensive documentation and user-friendly interfaces make it a good choice for beginners.
- Nginx and LiteSpeed may have steeper learning curves but offer greater control and performance benefits.
4. Budget:
- Consider your budget, as LiteSpeed may require licensing fees for the most feature-rich version.
- Apache and Nginx are open-source and free to use.
5. Community and Support:
- Apache has a vast user base and extensive community support.
- Nginx also has a robust community, while LiteSpeed’s community is smaller.
Summing Up
In the end, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of which web server is right for you. Your choice should depend on your specific needs, resources, and expertise.
- Choose Apache if you value stability, a wealth of documentation, and ease of use.
- Choose Nginx if you require high performance, efficiency, and are comfortable with a steeper learning curve.
- Choose LiteSpeed if you need performance, security features, and are willing to invest in a paid solution.
Ultimately, all three web servers are capable of serving web content effectively, and your choice should align with your website’s unique requirements and your level of technical expertise. Choose the right web server for you and then find a reliable web hosting company that provides the web server technology you need!
